Islam : Overview of the religion !
The meaning of the word Islam :
Islam is an Arabic word meaning "submission (to God)" and is described as a "Deen" in Arabic, meaning "way of life" and/or "religion". It has an etymological relationship to other Arabic words, such as Salaam, meaning "peace". The Arabic word "Muslim" is related to the word Islam and means a "vassal" of God and "one who surrendered" or submits (to God). Muslims see homage to God as a sign of distinction; this term has no negative connotations. Homage means serving the will of God above and beyond one's own goals.
Beliefs :
Islam has a number of beliefs that it teaches one to adhere to.
God :
The cornerstone of Islamic faith is a strict belief in monotheism. God is considered one and without an equal. Every chapter of the Qur'an (except for two) begins with "In the name of God, the Beneficent, the Merciful". God describes Himself in Sura al-Ikhlas, (chapter 112): "Say: He is God The One, God The Eternal. He never begot, nor was begotten. There is none comparable to Him." See the entry on the 99 names of Allah for Muslim views on God's attributes.
Prophets :
Islam teaches that God may reveal His will to mankind though an angel; such recipients of revelation are known as prophets. Islam makes a distinction between "prophets" and "messengers". Although all messengers are prophets, not all prophets are messengers.
Notable prophets include Adam, Noah, Abraham, Moses, Jesus and Muhammad, all belonging to a succession of men guided by God. Muhammad is viewed as the 'Last Messenger', bringing the final message of God to all mankind through the Qur'an. Messengers and prophets were sent to every nation and civilization, and every messenger was given a book for those people. These individuals were mortal humans; Islam demands that a believer accept all of the prophets, making no distinction between them. In the Qur'an, twenty five specific prophets are mentioned.
Islamic law :
The study of scripture is strongly emphasized. The Qur'an is the foremost source of Islamic jurisprudence, and the second is the Sunnah (Life and way of the Prophet). One cannot practise Islam without consulting both texts. From the Sunnah, related but not the same, come the Ahadith (narrations of the Prophet). A hadith is a narration about the life of the Prophet or what he approved - as opposed to his life itself, which is the Sunnah.
The Day of Judgement :
Other key beliefs include the Day of judgement, Heaven and Hell, the Angels, the Jinns (a species of invisible beings), the existence of magic (strictly forbidden to practice), the danger of evil eye (also forbidden), and the mercy, wisdom, and almighty strength of God.
The Six Elements of Belief :
There are several beliefs shared by all Muslims:
I- God (in Arabic, Allah)
II- Angels
III-Books (sent by God)
IV- Messengers (sent by God)
V- Day of Judgment
VI- Both good and evil (or more precisely, what people call good and evil) come from God. (Although in terms of Evil, it is more a product of people being misguided by the Devil.)
Religious authority :
There is no official authority who decides whether a person is accepted to, or dismissed from, the community of believers. Islam is open to all, regardless of race, age, gender, or previous beliefs. It is enough to believe in the central beliefs of Islam. This is formally done by reciting the shahada, the statement of belief of Islam, without which a person cannot be classed a Muslim. As no one can split open another's heart to see what's inside, it is enough to believe and say that you are a Muslim, and behave in a manner befitting a Muslim to be accepted into the community of Islam.
The Five Pillars of Islam:
The Five Pillars of Islam are five basic duties of Muslims:
I-The recitation and acceptance of the Creed (Shahada)
II- Daily prayer (Salat or Salah)
III- Paying alms (Zakat or Zakah)
IV- Observing the fast of Ramadan (Saum or Siyam)
V- Making the pilgrimage to Mecca (Hajj or Haj)
The Qur'an :
The Qur'an, also spelled Quran or Koran, is the holy book of Islam. Its title means "Recitation" or "Reading". It consists of 114 chapters or Surahs laid out roughly in order of size, the largest being near the front, the smallest near the back. It describes the origins of the Universe, Man, and their relationship to each other and their Creator. It sets out laws for society, morality, economics and many other topics. It is intended for recitation and memorization. The Qur'an is primarily taught from one generation to the next this way. Muslims regard the Qur'an as sacred and inviolable.
For Muslims, the Qur'an answers questions about daily needs, both spiritual and material. It discusses God and God's Names and attributes; believers and their virtues, and the fate of non-believers (kuffar); Mary, Jesus, and all the other prophets; and even scientific subjects. Muslims do not follow the laws of the Qur'an exclusively; they also follow the examples of the prophet, which is known as the Sunnah, and the understanding of the Qur'an contained in the teachings of the prophet known as the Ahadith. Muslims are taught that God sent down other books. Besides the Qur'an, the others are the book of Ibrahim (now lost) the Law of Moses (the Taurah), the Psalms of David (the Zabûr) and the Gospel of Jesus (the Injil). The Qur'an describes Christians and Jews as "the people of the Book" (ahl al Kitâb).
The teachings of Islam concern many of the same personages as those of Judaism and Christianity. However, Muslims frequently refer to them using Arabic names which can make it appear they are talking about different people: e.g. Allah for God, Iblis for Satan, Ibrahim for Abraham, etc. A belief in a day of judgment and an afterlife (Akhirah) are also part of Islamic theology.
The Qur'an is the word of God, sacred and immutable. Muslims do not touch the book unless in a state of ablution, known as "wudu." Muslims will typically keep it on a high shelf in their room, as a show of respect for the Qur'an, and some carry small versions with them for comfort or security.
The growth of Islam today :
Islam is the largest religion after Christianity. According to sources such as the World Network of Religious Futurists, the U.S. Center for World Mission, and the controversial Samuel Huntington, Islam is growing faster numerically than any other religion; the largest factor in this is natural population growth. It began in the Hejaz region of present-day Saudi Arabia in about 610, and according www.pewforums.org , it now comprises of 1.6 billion believers , 25% of the world's population, with almost 5 million believers in the USA. Only 15% of Muslims live in the Arab world.
Today , Islam has become the second global faith after Christianity..

Islamic laws:
Islamic law is called Shariah. Its main sources are the Qur'an and the Hadith, but ijma, the consensus of the community, was also accepted as a minor source. Qiyas, reasoning by analogy, was used by the law scholars (Mujtahidun) to deal with situations where the sources provided no concrete rules. The practices called Shariah today, however, also have roots in local customs (Al-urf).
The Islamic jurisprudence is called fiqh and is divided into two parts: the study of the sources and methodology (usul al-fiqh - roots of the law) and the practical rules (furu' al-fiqh - branches of the law).
Dietary laws :
When eating meat, Muslims may only eat from meat that has been slaughtered in the name of God, and meets stringent dietary requirements. Such meat is called pure, or halal. Islamic law prohibits a Muslim from eating pork, monkey, dog, cat, any carnivores, and several other types of animal, as these animals are haram (forbidden). For the meat of an animal to be halal (lawful) it must be one of the declared halal animals, it must be slaughtered by a Muslim, and the animal may not be killed by any cruel or prolonged means. The animal is killed by slicing the jugular veins, and thus rendering the animal unconscious immediately, the blood then flows out from the body, and the animal dies in its sleep. Some Muslim clerics have ruled that the animal does not have to be killed by a Muslim, but may be slaughtered by a Jew as long as it meets their strict dietary laws. Thus, some observant Muslims will accept kosher meat (meat prepared in accord with Jewish law) as halal.
The role of women in Islam :
Islam started in 7th century in the tribal society of Arabia. In those times , Arabs used to bury their daughters alive. After the advent of Islam, Arabs got revolutionized. Islam explicitly gives women these rights :
1-Right to education
2-Right to divorce (even on the basis of sexual dissatisfaction)
3-Right to property and inheritance.
4-Right to do independent business
Today , many people blames Islam for many bad practices of the Muslim societies such as honor killings or women rights in Saudi Arabia etc but all this has nothing to do with Islam. Cultural practices should not be mixed with the religion.
Islam does not prohibit women from working, but emphasizes the importance of caring for house and family for both parents. In theory, Islamic law allows each spouse to divorce at will, by saying "I divorce you" three times in public. In practice divorce is more involved than this and there may be separate state proceedings to follow as well. This practice is valid within most of the Muslim world today. Usually, the divorced wife keeps her dowry from when she was married, if there was one, and is given child support until the age of weaning at which point the child may be returned to its father if it is deemed to be best.
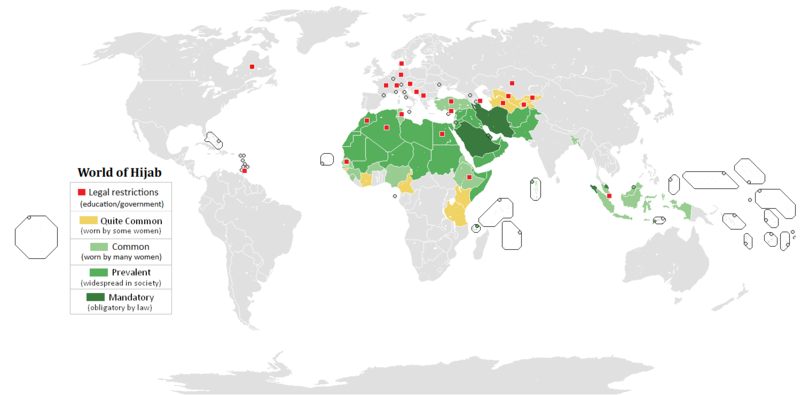
Dress Code :
The Qur'an also places a dress code upon its followers. For women, it emphasizes modesty without an overt call for any specific covering of any body part; men have a dress code which is more relaxed: the loins must be covered from knee to waist. The rationale given for these rules is that men and women are not to be viewed as sexual objects.
Islamic Dress code is a global phenomenon ... People residing in different countries all over the global adhere to Islamic Dress Code , in one form or the other..
Circumcision :
Circumcision for males involves the removal of the foreskin and is customary in most Muslim communities. It is normally performed at different ages in different cultures. Female circumcision is not part of mainstream Islam on an international scale, but is performed by Muslims and non-Muslims alike across East Africa and the Nile Valley, as well as parts of the Arabian peninsula. In both areas, the custom predates Islam. Many African Muslims believe that female circumcision is required by Islam, although no such custom is alluded to in the Quran, and no hadith exists purporting to mandate it.
Holidays :
Friday is an important day in the life of a Muslim and it is believed that any devotional acts done on this day gain a higher reward. This day however should not be understood as a Sabbath, for Muslims reject the belief that God rested after Creation. Believers attend congregational prayer at the local mosque, perform prayer and listen to a sermon by the Imam. When the holidays occur, it is according to the lunar Islamic calendar. This calendar does not correct for the fact that the lunar year does not match the solar year. Therefore, the Islamic months precess each year; they shift relative to the Gregorian calendar.
Ramadan - month long observance of fasting during daylight hours.
Feast of Breaking the Fast (Eid-ul-Fitr), or the Little Feast (al-Eid saghir)- occurs at the conclusion of Ramadan and is held on the first day of the month of Shawwal.
The Big Feast, (Eid-ul-Adha), also "The Feast of Sacrifice" (Kurban Bayram) - two months and 10 days after the Little Feast. Animals are slaughtered to commemorate Abraham's sacrificing of a ram instead of his son Ismael. Those who are able make a pilgrimage to Mecca do so just before this date, on the Hajj.
Ashura - the 10th day of the month of Muharram This is the day on which God saved Moses and the Jews from Pharaoh in Egypt as he crossed the Red Sea (the Exodus day). The prophet Muhammad (PBUH) is reported to have fasted along with the neighboring Jewish communities on this occasion, and according to narrations, Muhammad planned on fasting on the 9th and 10th of Muharram. This is also the day on which Muhammad's grandson, Husayn, was killed in in the Battle of Karbala. For Shi'a Muslims this is a day of mourning. Many Sunni Muslims also commemorate this event, albeit in a less dramatic fashion than the Shi'a. The observance of this day is frowned upon by fundamentalists.
Muslim New Year - not generally celebrated as an official Islamic holiday, although many Muslim communities have devised or revived some kind of new year ritual celebration. This celebration is frowned upon by fundamentalists.
The Prophet's Birthday (Al-Mawlidu N-Nabawi Sh-Sharif) - Some scholars consider this holiday to be an innovation in the religion, as Muhammad himself did not celebrate it, except by fasting. This holiday is prohibited by the Islamist movement (fundamentalist Islam). Some Arab nations, such as Saudi Arabia forbid Muslims to celebrate this holiday.
----------------
Please make this thread sticky.
Last edited:

